The aviation industry is constantly evolving and needs many qualified people to guarantee the efficiency and safety of air travel. Pilots and flight attendants are important field members and must complete training programs to carry out their duties effectively and professionally. For a more convenient reading experience with access to millions of books, check out this reading application.

Pilot Training
Aviation enthusiasts find flying to be an exciting experience worldwide. Training programs designed to prepare aspiring aviators are carefully built to grow aspiring pilots into skilled professionals capable of flying confidently and precisely in any environment. Their curriculum covers various topics, including emergency procedures, navigation skills, aerodynamics and aircraft systems, and aviation history lessons.
Private Pilot License
The first stage in every pilot's training process is obtaining a private pilot license (PPL), which gives holders all the abilities and information required to operate an aircraft for pleasure. PPL training includes the fundamentals of aviation, aerodynamics, aircraft systems, navigation, and flight maneuvers. Students then get hands-on flight experience under the supervision of a qualified flight instructor, which allows them to become proficient in smoothly and accurately handling an aircraft.

Commercial Pilot License
A Commercial Pilot License (CPL) is required for professional pilots who want to begin or continue their employment as professional aviators. Students also get in-depth training in emergency protocols, flight planning, and navigation skills, which equips them for the particular requirements of commercial aviation. The CPL training program strengthens PPL education by refining flight abilities and increasing competency in flight maneuvers.
Instrument Rating
An instrument rating (IR) is an essential part of pilot training for those hoping to fly commercially, particularly those looking at commercial flight aspirations. With this certification, pilots will learn to navigate aircraft solely using flight instruments in adverse weather conditions or low visibility, providing safer flying in adverse and low visibility conditions. Training for an instrument rating includes simulation scenarios for instrument flight practice with precision approaches and procedures designed for conducting safe instrument flight procedures.

Airline Transport Pilot License
The ultimate qualification accessible to pilots looking to work for commercial airlines is the Airline Transport Pilot License (ATPL), which represents the highest standard of pilot training. Three areas essential to commercial aviation's functioning are airline operations, crew resource management, and advanced flight capabilities, all of which are covered in ATPL training. Candidates undergo rigorous training to show they are proficient in various commercial aviation-related topics, including complicated aircraft systems, flight planning under duress, and making decisions under time restrictions.
Flight Attendant Training
In the aviation industry, flight attendants are essential because they give passengers comfort, safety, and security during their journey. Training programs are created especially to prepare people for work as flight attendants, and they are intended to cover every scenario that might come up while they're doing their tasks in flight, from handling emergency circumstances to giving exceptional customer service.

Safety and Emergency Procedures
Safety in aviation is of utmost importance, so flight attendant training starts by providing comprehensive instruction in safety and emergency procedures. Candidates learn to operate emergency equipment, evacuate aircraft in different circumstances, administer first aid treatment to passengers as necessary, and respond appropriately to security threats onboard aircraft. Particular emphasis is given to maintaining calm communication during emergencies to protect passenger safety and crew welfare.
Customer Service Hospitality
Flight attendants undergo customer service and hospitality training to create an exceptional passenger experience onboard the plane. Training topics may include passenger interaction, conflict resolution, cultural sensitivity, and service etiquette; flight attendants learn how to anticipate and meet passenger needs efficiently and professionally while creating a welcoming atmosphere onboard.

Cabin Crew Resource Management Training
CRM training is the cornerstone of flight attendant education, emphasizing teamwork, communication, and situational awareness. Flight attendants learn to collaborate effectively with fellow crew members during inflight operations while communicating efficiently in flight operations and managing challenging situations collaboratively. CRM training facilitates crew coordination and decision-making, contributing to safety and efficiency during operations.
Cultural and Language Skills
Due to the international nature of air travel, flight attendants receive training in cultural awareness and language proficiency to effectively interact with passengers from diverse backgrounds. Training may cover cultural customs and norms and basic proficiency in common passenger languages spoken onboard. If you need professional writing assistance, see writepaperfor.me. Flight attendants strive to foster inclusivity and respect cultural diversity onboard to ensure that each passenger feels welcomed throughout their journey.

Conclusion: Navigating the Skies Skillfully
Professional aviation training is indispensable to successful flight attendants and pilot careers. Pilot programs equip aspiring aviators with the knowledge, skills, and experience for precision flying. In contrast, flight attendant courses equip individuals to ensure passenger security and comfort through exceptional inflight service delivery. Pilots and flight attendants together navigate the skies with precision and professionalism on behalf of excellent aviation.
Comments (0)
Add Your Comment
SHARE
TAGS
INFORMATIONAL Flight Training Pilot Commercial Airline Pilot Safety Aviation Commercial AviationRECENTLY PUBLISHED
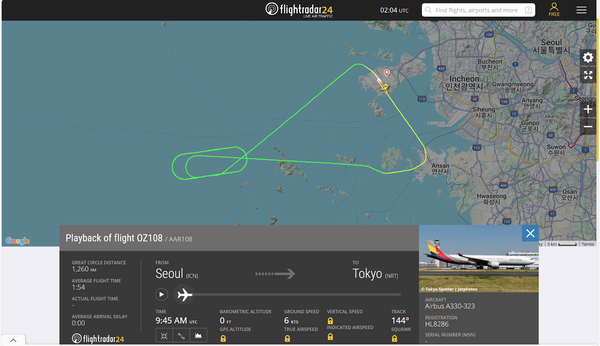 Tokyo-Bound Asiana Flight Experiences Engine Failure
An Asiana Airlines flight bound for Tokyo experienced an engine failure, prompting its return to Incheon International Airport.
NEWS
READ MORE »
Tokyo-Bound Asiana Flight Experiences Engine Failure
An Asiana Airlines flight bound for Tokyo experienced an engine failure, prompting its return to Incheon International Airport.
NEWS
READ MORE »
 Learjet Owned By Vince Neil Crashes Into Gulfstream Jet, 1 Fatality Confirmed
On February 10th, around 14:30 local time, a Learjet private jet aircraft crashed into another private jet after landing at Scottsdale Airport (SCF) in Arizona.
NEWS
READ MORE »
Learjet Owned By Vince Neil Crashes Into Gulfstream Jet, 1 Fatality Confirmed
On February 10th, around 14:30 local time, a Learjet private jet aircraft crashed into another private jet after landing at Scottsdale Airport (SCF) in Arizona.
NEWS
READ MORE »
 Seattle Plane Strike 2025: Japan Airlines and Delta Collision Raises Safety Concerns
Seattle-Tacoma International Airport saw a concerning incident on Wednesday morning when a Japan Airlines (JAL) plane clipped a parked Delta Air Lines jet while taxiing. Thankfully, no one was injured, but passengers described the collision as a frightening experience.
NEWS
READ MORE »
Seattle Plane Strike 2025: Japan Airlines and Delta Collision Raises Safety Concerns
Seattle-Tacoma International Airport saw a concerning incident on Wednesday morning when a Japan Airlines (JAL) plane clipped a parked Delta Air Lines jet while taxiing. Thankfully, no one was injured, but passengers described the collision as a frightening experience.
NEWS
READ MORE »



